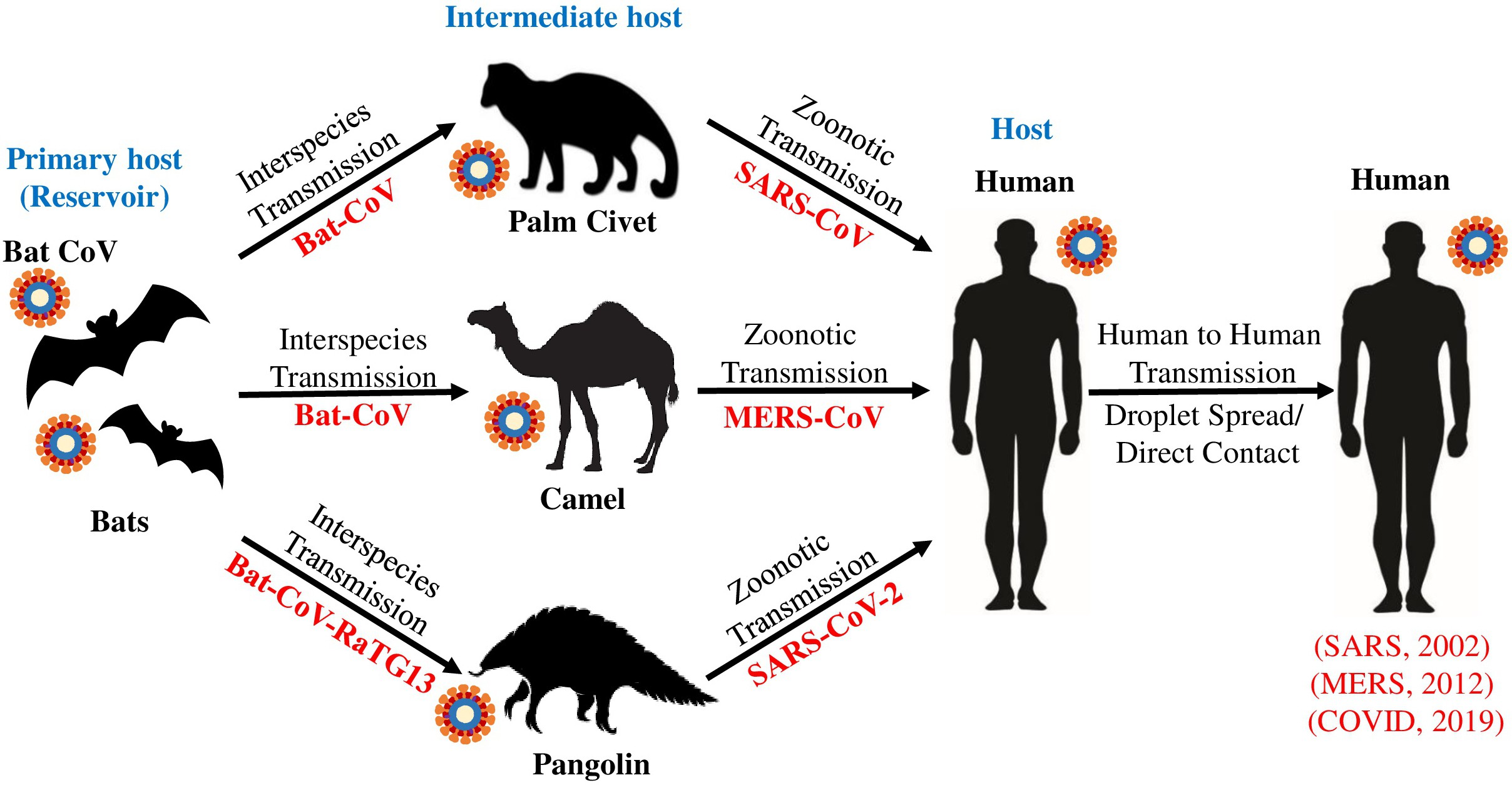
Fig. 1. Transmission path of coronaviruses (CoV). The family of coronaviruses has caused two major outbreaks in the last two decades, the SARS-CoV epidemic in 2002-2003 and the MERS-CoV in 2012. SARS-CoV, caused by the zoonotic transmission from palm civet was infected by interspecies transmission from wild bats, which spread to humans by droplet spread or direct contact. MERS-CoV infection resulted from zoonotic transmission from dromedary camels, which was later transmitted to humans. Similarly, the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus is believed to have jumped from bats to humans via pangolins at the end of 2019 at a local seafood market in Wuhan, China. The virus is transmitted between individuals by direct contact with respiratory droplets of an infected individual.